Key Takeaways
- Dental X-rays and diagnostics tools that help dentists detect hidden oral health issues.
- Different types of X-rays serve various purposes in dental care
- Modern digital X-rays offer reduced radiation exposure and improved image quality
- Regular X-rays are important for preventive care and early detection of dental problems
- X-ray frequency depends on individual risk factors and oral health history
- Dental X-rays are safe when used appropriately, with minimal radiation exposure
Dental X-rays and diagnostics tools allow dentists to see beyond what’s visible to the naked eye. These images help identify hidden dental problems, plan treatments, and monitor oral health over time. Let’s take a closer look at how dental X-rays and diagnostics work and why they’re so important for maintaining a healthy smile.
Understanding Dental X-rays and Diagnostics
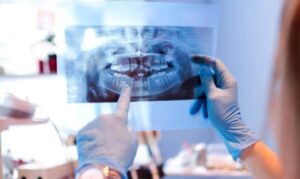
Dental X-rays are images that show the structures inside your mouth, including teeth, bones, and soft tissues. They use low levels of radiation to create detailed pictures that help dentists spot issues that might not be apparent during a visual exam.
How Dental X-rays and Diagnostics Work
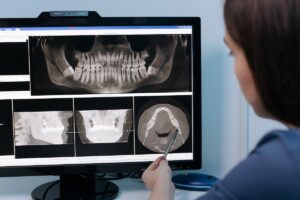
Dental X-rays and diagnostics are essential tools that help dentists see beyond the surface of your teeth and gums. X-rays use safe, low levels of radiation to capture detailed images of the teeth, bones, and surrounding tissues, revealing issues like cavities, bone loss, infections, or impacted teeth that might not be visible during a regular exam.
Different types of X-rays, such as bitewing, panoramic, and periapical, offer various views and details, allowing dentists to create a precise treatment plan. Together with other diagnostic methods, X-rays play a key role in preventive care and early detection, helping maintain oral health effectively.
X-rays pass through soft tissues like gums and cheeks but are absorbed by denser materials like teeth and bone. This creates a contrast that allows dentists to see the internal structures of your mouth. The images can reveal cavities, bone loss, and other hidden problems.
Types of Dental X-rays
There are several types of dental X-rays, each serving a specific purpose:
- Bitewing X-rays: These show the upper and lower back teeth in a single view. They’re useful for detecting decay between teeth and assessing bone levels.
- Periapical X-rays: These provide a view of the entire tooth, from the crown to the root. They help identify problems below the gum line or in the jaw.
- Panoramic X-rays: These create a single image of the entire mouth, including all teeth, both jaws and surrounding structures. They’re often used for planning treatments like braces or implants.
- Occlusal X-rays: These show the floor or roof of the mouth and are used to find extra teeth, cysts, or other abnormalities.
Digital vs. Traditional X-rays
Many dental offices now use digital X-rays instead of traditional film X-rays. Digital X-rays offer several advantages:
- Lower radiation exposure (up to 80% less than traditional X-rays)
- Instant image availability
- Easy storage and sharing of images
- Ability to enhance and manipulate images for better diagnosis
The Importance of Dental X-rays and Diagnostics
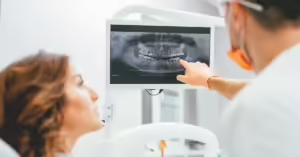
Dental X-rays and diagnostics play a crucial role in maintaining long-term oral health by catching problems early—often before symptoms arise. These imaging tools allow dentists to detect hidden issues such as cavities between teeth, bone loss, infections, and even tumors that would otherwise go unnoticed during a standard exam.
By identifying these concerns early, dentists can develop targeted treatment plans that prevent minor issues from escalating into more complex, costly, or painful problems. From bitewing to panoramic views, each type of X-ray offers unique insights into the structure and health of your mouth.
In combination with regular exams, dental X-rays are a powerful preventive measure, ensuring a healthier smile and often reducing the need for extensive future treatments. Dental X-rays play a crucial role in diagnosing and treating oral health issues. They allow dentists to:
Detect Hidden Decay
X-rays can reveal cavities that are not visible during a regular dental exam, especially between teeth or under existing fillings.
Identify Gum Disease
X-rays show changes in bone density that can indicate periodontal disease, even before symptoms are noticeable.
Spot Infections
Abscesses and other infections can be detected on X-rays, helping dentists provide timely treatment.
Plan Dental Procedures
X-rays are essential for planning treatments like root canals, implants, and orthodontic work.
Monitor Tooth Development
For children and teenagers, X-rays help track the growth and positioning of permanent teeth.
Frequency of Dental X-rays
The frequency of dental X-rays depends on various factors, including:
- Age
- Current oral health
- Risk for dental disease
- History of dental problems
Typical X-ray Schedules
Here’s a general guideline for X-ray frequency:
- Children: Every 6-12 months
- Teens: Every 6-18 months
- Adults with good oral health: Every 2-3 years
- Adults with ongoing dental issues: More frequently, as recommended by the dentist
It’s important to note that these are just guidelines. Your dentist will create a personalized X-ray schedule based on your specific needs.
Safety Considerations for Dental X-rays
Dental X-rays are considered safe when used appropriately. The amount of radiation exposure from dental X-rays is very low, especially with modern digital systems.
Radiation Exposure Comparison
To put dental X-ray radiation in perspective, here’s a comparison of radiation exposure from various sources:
| Source | Radiation Exposure (microsieverts) |
|---|---|
| Single digital dental X-ray | 1-8 |
| Chest X-ray | 100 |
| Mammogram | 400 |
| Daily natural background radiation | 10 |
As you can see, the radiation from a dental X-ray is minimal compared to other common sources.
Protective Measures
Dentists take several precautions to minimize radiation exposure:
- Using lead aprons to shield the body
- Focusing the X-ray beam on a small area
- Using fast film or digital sensors to reduce exposure time
- Taking X-rays only when necessary
Dental X-rays for Special Populations
Some groups require special consideration when it comes to dental X-rays:
Pregnant Women
While dental X-rays are generally safe during pregnancy, they’re usually postponed unless necessary. If needed, extra protective measures are taken.
Children
Children may need more frequent X-rays to monitor tooth development, but dentists use lower radiation doses and take extra precautions.
Patients with Dental Implants
People with dental implants may need more frequent X-rays to monitor the implants and surrounding bone.
Beyond X-rays: Advanced Dental Diagnostics
While X-rays are a fundamental diagnostic tool, dentists also use other advanced technologies for diagnosis and treatment planning:
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT)
CBCT creates detailed 3D images of the mouth, teeth, and jaws. It’s particularly useful for:
- Planning dental implant placement
- Evaluating jaw disorders
- Assessing complex root canal cases
Intraoral Cameras
These tiny cameras allow dentists to take close-up images of teeth and gums, helping to detect issues and explain findings to patients.
Laser Cavity Detection
Special lasers can detect early signs of tooth decay, often before they’re visible on X-rays.
The Role of Dental X-rays in Preventive Care
Dental X-rays are a key component of preventive dental care. They allow dentists to:
Catch Problems Early
By detecting issues before they become severe, X-rays help prevent more extensive and costly treatments down the line.
Track Changes Over Time
Comparing X-rays from different visits allows dentists to monitor changes in oral health and catch developing problems.
Educate Patients
X-rays provide a visual tool for dentists to explain oral health issues to patients, improving understanding and compliance with treatment plans.
Interpreting Dental X-rays
While dentists are trained to interpret X-rays, it can be helpful for patients to understand what they’re looking at:
Common Features of Dental X-rays
- Teeth: Appear as the brightest white areas
- Fillings: Show up as even brighter white areas within teeth
- Bone: Appears as a lighter shade of gray
- Decay: Often shows up as dark spots within the bright white of the tooth
Digital X-ray Enhancements
Digital X-ray systems allow dentists to:
- Zoom in on specific areas
- Adjust the contrast for better visibility
- Use color-mapping to highlight different structures
These features can make it easier for both dentists and patients to understand what the X-rays reveal.
The Future of Dental Diagnostics
As technology advances, we can expect to see continued improvements in dental diagnostic tools:
Artificial Intelligence in X-ray Interpretation
AI algorithms are being developed to assist dentists in analyzing X-rays, potentially improving accuracy and efficiency in diagnosis.
3D Printing from X-ray Data
Advanced imaging techniques combined with 3D printing technology may allow for more precise treatment planning and custom dental appliances.
Improved Radiation-free Imaging
Research is ongoing into new imaging technologies that could provide detailed oral health information without using radiation.
Making the Most of Your Dental X-rays
To get the most benefit from dental X-rays:
- Keep a record of your X-rays and when they were taken
- Inform your dentist of any changes in your health history
- Ask questions about what the X-rays show and what they mean for your oral health
- Follow your dentist’s recommended X-ray schedule
Overcoming X-ray Anxiety
Some patients feel anxious about getting dental X-rays. Here are some tips to help:
- Communicate your concerns with your dentist
- Ask about the safety measures in place
- Request explanations about why each X-ray is necessary
- Consider bringing a comfort item (like headphones with music) to help you relax
The Cost of Dental X-rays
The cost of dental X-rays can vary depending on the type of X-ray and your location. Here’s a general price range:
| Type of X-ray | Average Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Bitewing (set of 4) | $20 – $100 |
| Full mouth series | $85 – $250 |
| Panoramic | $60 – $150 |
Many dental insurance plans cover routine X-rays as part of preventive care. Check with your insurance provider for specific coverage details.
Conclusion:
Dental X-rays and diagnostics are crucial tools in maintaining good oral health. They allow dentists to detect and treat problems early, potentially saving patients from more extensive and expensive procedures down the line. While it’s natural to have questions about radiation exposure, the benefits of dental X-rays far outweigh the minimal risks when used appropriately.
By understanding the importance of dental X-rays and working with your dentist to determine an appropriate X-ray schedule, you can take a proactive approach to your oral health. Remember, these diagnostic tools are just one part of a comprehensive dental care plan that includes regular check-ups, good oral hygiene practices, and a healthy lifestyle.
